RainbowSingularity
Valued Senior Member
it looks like calving is accelerating (as i suspected)
i wonder if it is exponentially speeding up.
what are the implications ?
global impacts commercial/financial/transport ?
what are the environmental impacts ?
it looks like melting is speeding up
as these ice shelves are broken off they will allow glaciers to speed up & calve faster
(so scientists have suggested)
https://www.livescience.com/brunt-ice-shelf-breaks-antarctica.html

i wonder if it is exponentially speeding up.
what are the implications ?
global impacts commercial/financial/transport ?
what are the environmental impacts ?
it looks like melting is speeding up
as these ice shelves are broken off they will allow glaciers to speed up & calve faster
(so scientists have suggested)
https://www.livescience.com/brunt-ice-shelf-breaks-antarctica.html
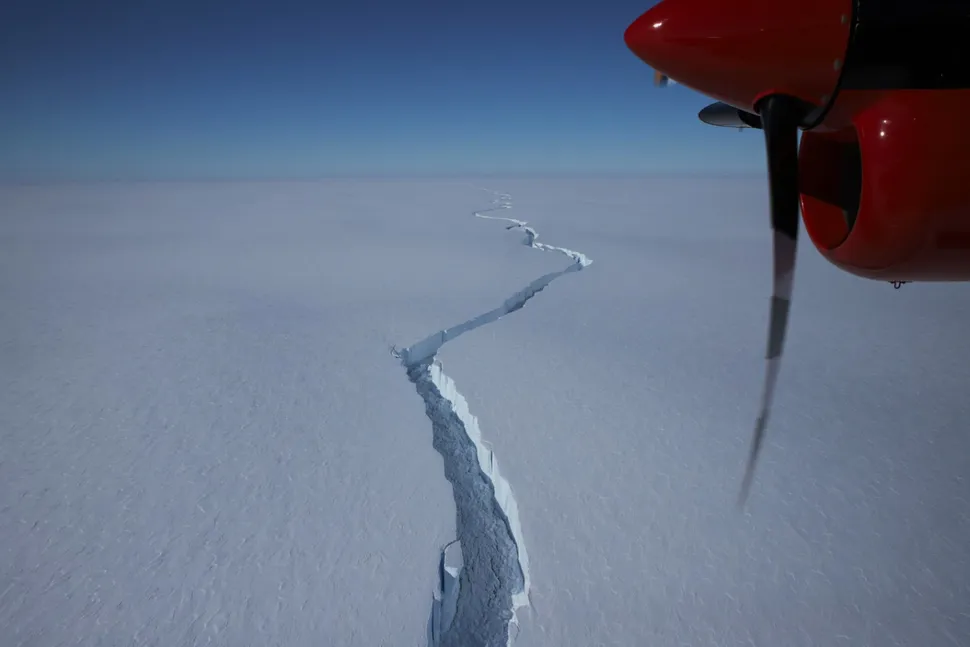
Giant crack frees a massive iceberg in Antarctica
By Yasemin Saplakoglu - Staff Writer a day ago
A giant iceberg, more than 20 times the size of Manhattan, just split off from Antarctica's Brunt Ice Shelf.