Here goes:
A1: Complex numbers exists. Call this C.
A2: x = x
A3: x + y = y + x
A4: A is a subset of B if B contains A and B - A not = the empty set.
Index.....Statement...…………………………………………………………………………………….. Reason
1...…...….Construct S = C x C.......................................................................................A1, A2
1.1...…….S is 4 dimensional....................................................................................…...1
1.2.........Set the components of S = S_1,2,3,4 in the following order: Re, Im, Re, Im.....1, A2
2......…...S can transform into two Riemann Spheres......................................……...A1, 1
3............Construct two Riemann Spheres in S, call it RS x RS = Pp......................…..A1, 1
4............Isolate the Riemann Circle of S_3, 4 and call it P_T.................................…A1, 3
4.1......…I'm going to use physical terminology below........................................…..Declaration
4.2...…..Construct "physical space" = S_P = CxC/S_4.......................................…...…A1, A2
5......…..Let P_T advance by one (rotate relative to S1,2,3) when encountering a space node and let the rotation be a quantum rotation. Call this "freq" = T_S......................….............A1, 4, 4.2, A2
7......…..Define "Change in freq" by T_Sf - T_Si…………………………………....5
8...........Let S_1,2 be perpendicular to S_3,4.................................................................1
11..........Construct {for all n = 1 to N: n(T_Sf - T_Si)} . Call this "Changes in freqs.".........5,7
12.........Define "basic time interval" = Delta t_B = 1/[(1/N) \sum \limits_{n=1}^N n(T_Sf - T_Si)]...........................................................................................................................1-11, A3, A2
13.......Construct MxT_S, M element of Natural Numbers subset of C..................................5, A4
14.......Define " Basic time" = t_B = {1/[(1/M) (\sum \limits_{n=1}^M n#T_S)]}*Delta t_B...............12, 5, A3
15........Couple t_B to every node of S_P and call the result "basic spacetime"= B_ST...........4.2, A2, A2
15.1......Construct S_i = CxC........................................................................................A1
16........Construct RSxRS in S_i, call it Pp..................................................................15.1, 2
17........Isolate the Riemann Circle in Pp and call it P_BT....................................................A1, 16
18........Let P_BT advance by one (rotate relative to S_i1,2,3) when encountering A B_ST node and let the rotation be a quantum rotation. Call this "freq2"= T_BST.................................17, A2
19........Construct KxT_BST, K element of Natural Numbers, subspace of C........................18, A4
20........Define "Tim1" = t_1 = 1/[(1/K)(\sum \limits_{n=1}^K n#T_BST)]..............................A3, A2, 18
21.......Pp is in every particle of the clock..........................................................................Requirement
22......."Tim1" advances like a clock, it depends on the Pp in the clock and on the route in B_ST.................................................................................................................................18, 21
23......."Tim1" = Time........................................................................................................A2, 22
Further:
24.........Define a constant c = DS_P/Dt_B........................................................................4.2, A2
24.1......Let c be the maximum speed trough B_ST i.e. the speed at which the particle sees no distance between succeeding nodes of B_ST..................................................................4.2
24.1......Define an operator: "<->" as "superposition operator".......................................1, 2
24.2......Construct S = CxC from a copy of B_ST................................................................A1
25.........From S, define a new RS <-> RS, subject to item 32.2..........................................24.2
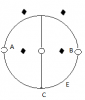
29.........Construct S_AP = (-C)x(-C)2)...............................................................................A1
30.........Construct from S_AP a RS_AP <-> RS_AP. Call it F_1............................................29, 2
31.........Construct any given vector in a RS <-> RS set = F_1, call it "four-momentum" = p. This is done by identifying four numbers in F_1. Call such particle qFp_1.1).........................3, 18, 4.1
32..........p is 4 dimensional.............................................................................................31
33..........Construct the same vector as in 31 x (-1) in F_1. Call such particle qFp_1............31, 28
34 Identify a marker in F_1's origin and at the origin in F_1.......................................31, 33
35..........Set FP_1 = qFp_1 and leave out 4 distinguised points just below the unit circle crossing a curled up axis. Call the four points c_1, c_1, c_2, c_2.........................................24.2
36..........Set Fp_1 = qFp_1 and leave out 4 distinguised points just below the unit circle crossing a curled up axis. Call the four points c_1, c_1, c_2, c_2.........................................29
37.........Let S_1, S_2 of Fp_1 look like in Figure 1.1........................................................24.2, 35
Figure 1.1
38..........Let S_AP1, S_AP2 of Fp_1 look like in Figure 1.1, (just turned upside down)..29 -> 32.1
39..........Let the starting position (after one instance of time) of Fp_1 and Fp_1 be as drawn in figure 1.2 (only the curled up x and y-direction shown).................................................29
Figure 1.2
40..........Let the four points c_n sense the closest four nodes of B_ST in direction p and let them engage these nodes even if the whole Fp_1 needs to turn or move linearly...………………………….....35
41.........If four nodes were engaged: distinguish four new nodes and go to 40...........35
42.........Let Fp_1 move similarly to 40, just sensing nearest nodes of negative coordinates in the down direction....................................................................................................35
43.........Fp_1 and Fp_1 may be polarised: cicularly, transversely or longetudinally......37
45.........Fp_1 has spin 1...............................................................................................44
46.........The nodes of B_ST causes a force with nonzero component in the up direction. Define F = ma. With m = 0 we have infinite acceleration thus infinite speed. But infinite speed is just c. Hence Fp_1 goes upwads at the speed of light.........................................................24.2, 37
47..........That the movement of Fp_1 causes Electro magnetic waves can be seen from the following figure. The F forces have a tiny reaction force in the up direction...............figure 1.3
Figure 1.3
48.........Fp_1 is a photon ...............................................................................................43 -> 47
Comments:
1) We construct particles in theory, we construct them first as particles to see what the machinery of particles is. We will later construct only in particle-antiparticle pairs. Note that by figure 1.2 momentum of Fp_1 in down direction is prohibited.
2) This way the particle and antiparticle may look identical except for phase difference of 180 degrees.
A1: Complex numbers exists. Call this C.
A2: x = x
A3: x + y = y + x
A4: A is a subset of B if B contains A and B - A not = the empty set.
Index.....Statement...…………………………………………………………………………………….. Reason
1...…...….Construct S = C x C.......................................................................................A1, A2
1.1...…….S is 4 dimensional....................................................................................…...1
1.2.........Set the components of S = S_1,2,3,4 in the following order: Re, Im, Re, Im.....1, A2
2......…...S can transform into two Riemann Spheres......................................……...A1, 1
3............Construct two Riemann Spheres in S, call it RS x RS = Pp......................…..A1, 1
4............Isolate the Riemann Circle of S_3, 4 and call it P_T.................................…A1, 3
4.1......…I'm going to use physical terminology below........................................…..Declaration
4.2...…..Construct "physical space" = S_P = CxC/S_4.......................................…...…A1, A2
5......…..Let P_T advance by one (rotate relative to S1,2,3) when encountering a space node and let the rotation be a quantum rotation. Call this "freq" = T_S......................….............A1, 4, 4.2, A2
7......…..Define "Change in freq" by T_Sf - T_Si…………………………………....5
8...........Let S_1,2 be perpendicular to S_3,4.................................................................1
11..........Construct {for all n = 1 to N: n(T_Sf - T_Si)} . Call this "Changes in freqs.".........5,7
12.........Define "basic time interval" = Delta t_B = 1/[(1/N) \sum \limits_{n=1}^N n(T_Sf - T_Si)]...........................................................................................................................1-11, A3, A2
13.......Construct MxT_S, M element of Natural Numbers subset of C..................................5, A4
14.......Define " Basic time" = t_B = {1/[(1/M) (\sum \limits_{n=1}^M n#T_S)]}*Delta t_B...............12, 5, A3
15........Couple t_B to every node of S_P and call the result "basic spacetime"= B_ST...........4.2, A2, A2
15.1......Construct S_i = CxC........................................................................................A1
16........Construct RSxRS in S_i, call it Pp..................................................................15.1, 2
17........Isolate the Riemann Circle in Pp and call it P_BT....................................................A1, 16
18........Let P_BT advance by one (rotate relative to S_i1,2,3) when encountering A B_ST node and let the rotation be a quantum rotation. Call this "freq2"= T_BST.................................17, A2
19........Construct KxT_BST, K element of Natural Numbers, subspace of C........................18, A4
20........Define "Tim1" = t_1 = 1/[(1/K)(\sum \limits_{n=1}^K n#T_BST)]..............................A3, A2, 18
21.......Pp is in every particle of the clock..........................................................................Requirement
22......."Tim1" advances like a clock, it depends on the Pp in the clock and on the route in B_ST.................................................................................................................................18, 21
23......."Tim1" = Time........................................................................................................A2, 22
Further:
24.........Define a constant c = DS_P/Dt_B........................................................................4.2, A2
24.1......Let c be the maximum speed trough B_ST i.e. the speed at which the particle sees no distance between succeeding nodes of B_ST..................................................................4.2
24.1......Define an operator: "<->" as "superposition operator".......................................1, 2
24.2......Construct S = CxC from a copy of B_ST................................................................A1
25.........From S, define a new RS <-> RS, subject to item 32.2..........................................24.2
29.........Construct S_AP = (-C)x(-C)2)...............................................................................A1
30.........Construct from S_AP a RS_AP <-> RS_AP. Call it F_1............................................29, 2
31.........Construct any given vector in a RS <-> RS set = F_1, call it "four-momentum" = p. This is done by identifying four numbers in F_1. Call such particle qFp_1.1).........................3, 18, 4.1
32..........p is 4 dimensional.............................................................................................31
33..........Construct the same vector as in 31 x (-1) in F_1. Call such particle qFp_1............31, 28
34 Identify a marker in F_1's origin and at the origin in F_1.......................................31, 33
35..........Set FP_1 = qFp_1 and leave out 4 distinguised points just below the unit circle crossing a curled up axis. Call the four points c_1, c_1, c_2, c_2.........................................24.2
36..........Set Fp_1 = qFp_1 and leave out 4 distinguised points just below the unit circle crossing a curled up axis. Call the four points c_1, c_1, c_2, c_2.........................................29
37.........Let S_1, S_2 of Fp_1 look like in Figure 1.1........................................................24.2, 35
Figure 1.1
38..........Let S_AP1, S_AP2 of Fp_1 look like in Figure 1.1, (just turned upside down)..29 -> 32.1
39..........Let the starting position (after one instance of time) of Fp_1 and Fp_1 be as drawn in figure 1.2 (only the curled up x and y-direction shown).................................................29
Figure 1.2
40..........Let the four points c_n sense the closest four nodes of B_ST in direction p and let them engage these nodes even if the whole Fp_1 needs to turn or move linearly...………………………….....35
41.........If four nodes were engaged: distinguish four new nodes and go to 40...........35
42.........Let Fp_1 move similarly to 40, just sensing nearest nodes of negative coordinates in the down direction....................................................................................................35
43.........Fp_1 and Fp_1 may be polarised: cicularly, transversely or longetudinally......37
45.........Fp_1 has spin 1...............................................................................................44
46.........The nodes of B_ST causes a force with nonzero component in the up direction. Define F = ma. With m = 0 we have infinite acceleration thus infinite speed. But infinite speed is just c. Hence Fp_1 goes upwads at the speed of light.........................................................24.2, 37
47..........That the movement of Fp_1 causes Electro magnetic waves can be seen from the following figure. The F forces have a tiny reaction force in the up direction...............figure 1.3
Figure 1.3
48.........Fp_1 is a photon ...............................................................................................43 -> 47
Comments:
1) We construct particles in theory, we construct them first as particles to see what the machinery of particles is. We will later construct only in particle-antiparticle pairs. Note that by figure 1.2 momentum of Fp_1 in down direction is prohibited.
2) This way the particle and antiparticle may look identical except for phase difference of 180 degrees.
Attachments
Last edited: